How big is Ukraine’s nuclear power industry?
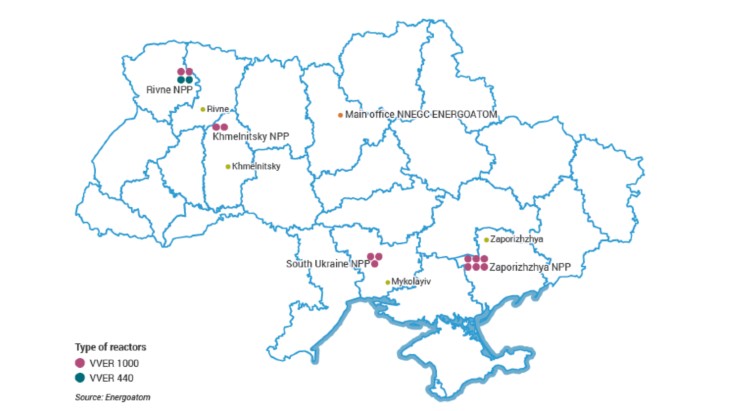
Ukraine is heavily dependent on nuclear energy, with 15 reactors generating about half of its electricity. All its current reactors are Russian-designed VVER types.
What is the history of nuclear power in Ukraine?
Nuclear development started in 1970, when Ukraine was part of what was then the Soviet Union, with the construction of the Chernobyl power plant. The first unit was commissioned in 1977 with unit 4 coming online in 1983. Following the accident in 1986, units 5 and 6 were cancelled in 1989.
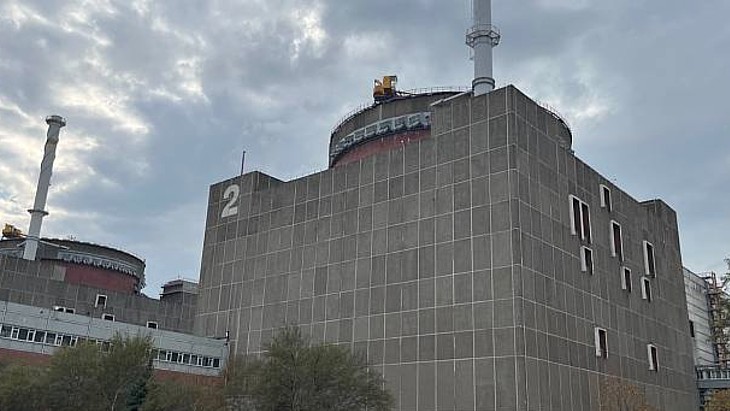
The industry remained relatively stable during the years when the country became independent of the former Soviet Union. At the end of 1995 Zaporozhe 6 was connected to the grid making Zaporozhe the largest nuclear power station in Europe, with a net capacity of 5700 MWe. (The second largest station operating is Gravelines, near Dunkerque in France, with a net capacity of 5460 MWe.)
In August and October 2004 Khmelnitski 2 and Rovno 4 respectively were connected to the grid, bringing their long and interrupted construction to an end and adding 1900 MWe to replace that lost by closure of Chernobyl units 1 and 3 in 1996 and 2000 respectively.
Click here to read more detail on Ukraine’s nuclear historyWhat plans has Ukraine had for new nuclear capacity?
The original design lifetime of the Russian reactors was 30 years, but work has taken place to allow a series of lifetime extensions.
In September 2021 the Ukrainian state-owned nuclear power firm Energoatom signed an agreement with the US-based firm Westinghouse to build four AP1000 reactors at established sites in the country. Since then Energoatom has outlined plans for further reactors - including exploring the possibility of deploying small modular reactors from US firm NuScale - as part of its goal of 24GWe of nuclear capacity by 2040.
What about Ukraine’s nuclear fuel?
Ukraine has access to two fuel suppliers: Russia's TVEL and Westinghouse. Most fuel in Ukraine’s reactors is manufactured by TVEL, but the country has had an ongoing project in recent years to diversify its fuel sources
As of mid-2021, six of Ukraine’s 15 reactors were operating using fuel manufactured by Westinghouse, fabricated at its plant in Västerås in Sweden.
What Energoatom said ahead of the latest events
Early in February Energoatom's CEO Petro Kotin said that: "According to the protocol, the plants will not work in case, for example, of bombing attack. In such a case, the plant is shut down and unloaded until the threat is eliminated.
"In the event of loss of the external power supply at the nuclear power plant, the autonomous power supply system starts working by means of powerful diesel generators. Ukrainian nuclear power plants are ready for such a mode of operation: the stock of diesel fuel located at nuclear power plants significantly exceeds the established standards.
"In addition, Ukrainian power units are ready even for an aircraft crash, because the containment and the reactor vessel designed to withstand corresponding risks."
He added that two years' worth of nuclear fuel had been stockpiled in case of interruption of supply.
The latest updates on the situation in Ukraine
8 April: IAEA seeks early visit to assess radiation levels around Chernobyl
4 April: Ukraine prepares to rotate Chernobyl staff
1 April: Ukraine says Russian forces have left Chernobyl
29 March: IAEA's Grossi in Ukraine for nuclear safety talks
28 March: Fresh concerns over staffing at Chernobyl
23 March: IAEA seeks information about forest fires near Chernobyl
21 March: First Chernobyl staff rotate, after 25 days
17 March: 'No safety concern' as Zaporozhe loses third power line
15 March: Power supply restored to Chernobyl
11 March: Detailed safety measures to be proposed after IAEA talks
7 March: IAEA concern over communication issues at Zaporozhe